
Background
In the field of building fire protection, concrete structures often face the dual effects of extreme high temperature burning and fire water spray cooling, which has a significant impact on the microstructure and fracture mechanical properties of concrete.
Recently, a research team from Shanghai University conducted an experimental study based on digital image correlation technology (DIC) and acoustic emission technology (AE) to analyze with high precision the effect of high-temperature rapid cooling on the fracture performance of high-performance concrete (HPC).
For details, see the paper " Study on the fracture mechanical properties of high performance concrete (HPC) with rapid cooling after high temperature "
Experimental Platform
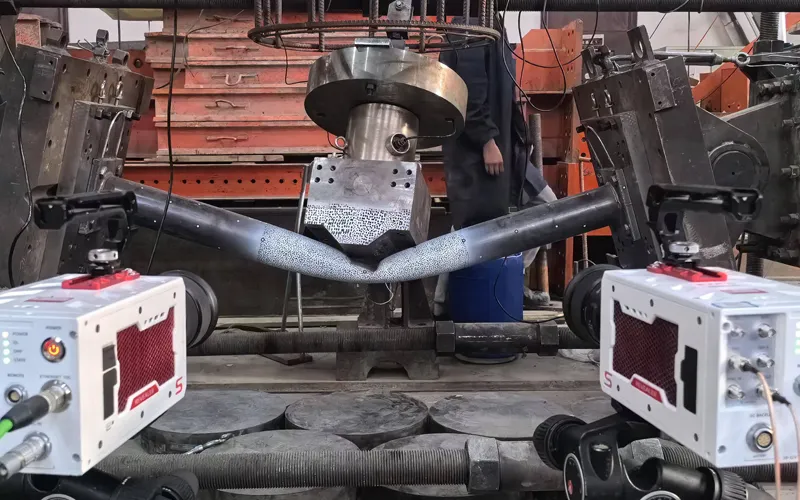
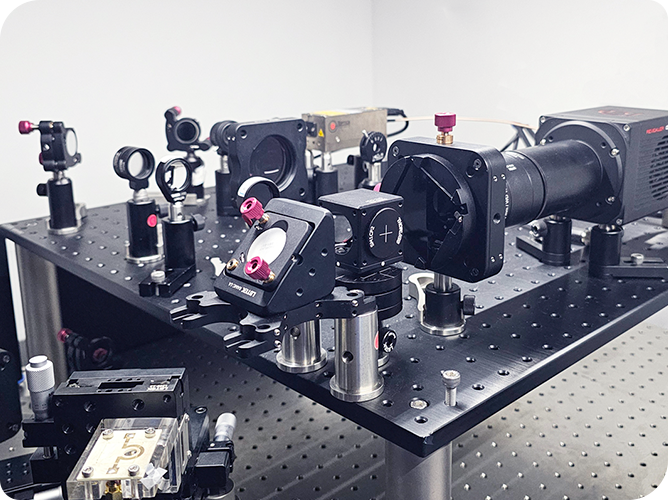
It consists of the Revealer DIC system and other supporting equipment.
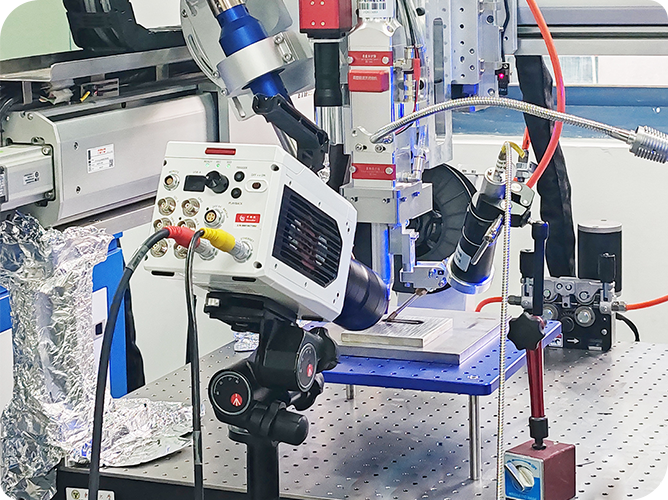
1. DIC measurement system: Revealer DIC 3D measurement equipment, including 2 ultra-high-definition high-speed cameras, see Figure 1. RDIC strain field analysis software, supports real-time generation of displacement and strain cloud maps, supports crack propagation analysis, can locate crack tips, and calculate opening angles.
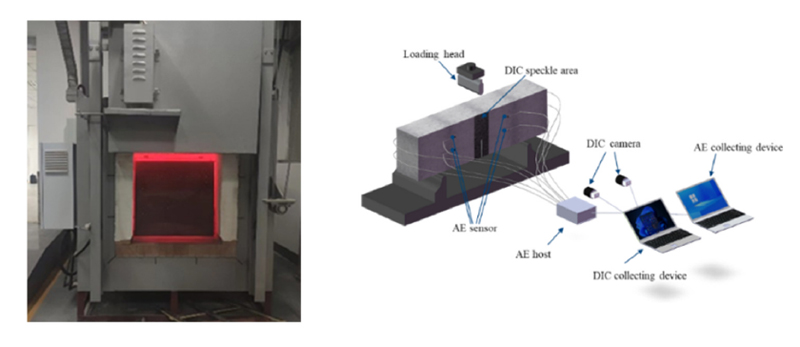
Figure 1 Revealer DIC measurement system
2. Supporting equipment:
1) High temperature furnace: up to 1000°C, temperature control accuracy ±1°C, simulating high temperature environment of fire.
2) Hydraulic servo: three-bending beam loading (0.3 mm/min displacement control), load sensor measuring range 0 kN~2000 kN , displacement sensor measuring range 0 mm~200 mm, extensometer measuring range 0 mm~10 mm, used for synchronous collection of load-displacement data.
3) Acoustic emission system: 50-400 kHz sensor to capture the acoustic signal of crack propagation.
Experimental procedures
1. Experimental Preparation
1.1 Specimen preparation: The research team prepared three-point bending beam specimens of two materials: ordinary concrete (PC) and high-performance concrete (HPC). The specimen dimensions were 550mm×150mm×100mm, the pre-cut length was 60mm, the cut height ratio was 0.4, the span was 450mm, and the span height ratio was 3.
1.2 High temperature and cooling treatment: After pre-drying, the specimens were treated at high temperature conditions of 20°C, 200°C, 400°C, 600°C and 800°C, and then immediately placed in a cooling pool for 90 minutes to simulate a fire sprinkler scenario.

Figure 2 Performance characteristics of concrete after high temperature
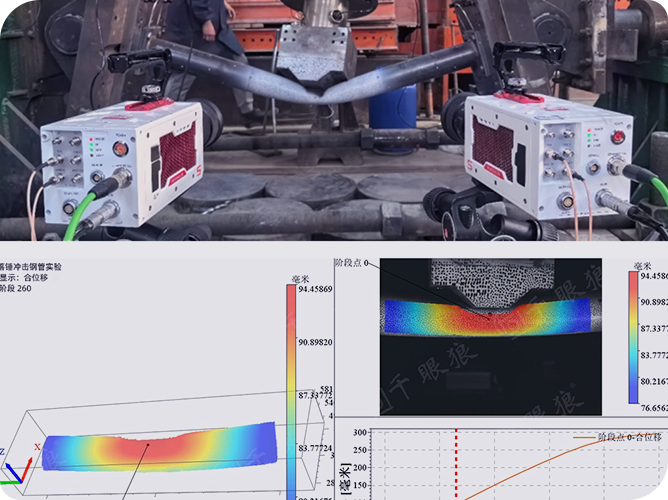
1.3 Loading test: The cooled specimens were subjected to a three-point bending beam loading test. The specimens were loaded at 0.3 mm/min using a hydraulic servo testing machine, and the speckle image of the specimen surface was collected by the DIC system. The load-time curve and displacement-time curve of the hydraulic servo machine were recorded at the same time, and the load-crack opening displacement CMOD value was recorded by an extensometer, which was highly consistent with the DIC measurement results, as shown in Figure 3.
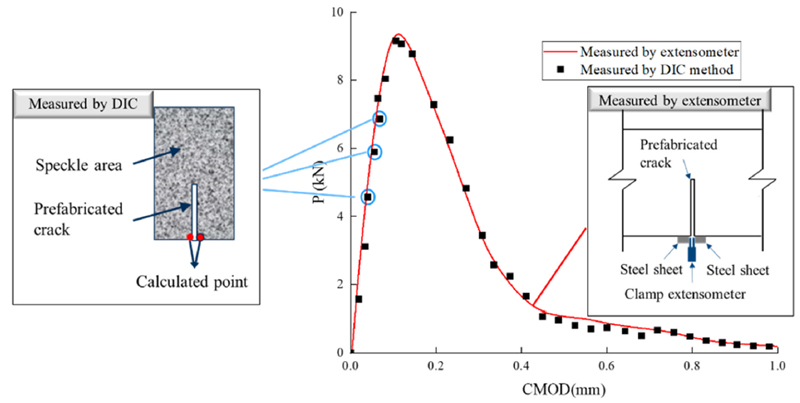
Figure 3 Comparison of CMOD values measured by DIC and extensometer
1.4 Data analysis: The collected images were analyzed by the DIC system, a line crack was drawn every 5 pixels , the lateral displacement jump point was analyzed, and the crack tip was located, as shown in Figure 4. At the same time, the damage process of concrete was analyzed by combining the acoustic emission (AE) technology.
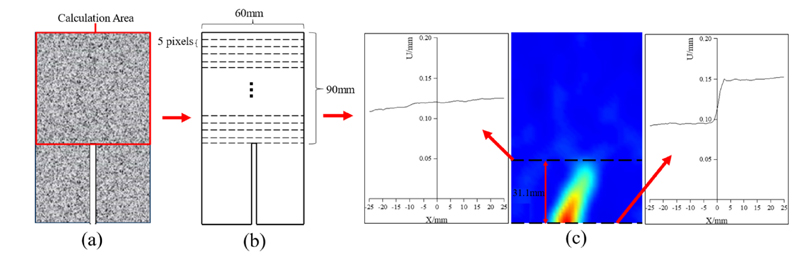
Fig.4 Schematic diagram of crack length calculation
Experimental Conclusion
The DIC measurement system analysis found that the HPC crack initiation stage significantly advances with temperature, from Pre-60% peak load at room temperature to Pre-10% at 800°C. DIC measured that the crack growth rate of HPC became uniform after 600°C, while PC softened at 200°C, proving that HPC has better interface density. At the same time, the DIC, extensometer, and AE measurement data were cross-verified, which also verified the reliability of non-contact measurement.
Experimental Outlook
Through the Revealer DIC measurement system, researchers have revealed the effects of different material compositions and proportions on the fracture performance of concrete. Under complex loading conditions, the DIC measurement system can monitor the deformation and crack development of concrete in real time, providing dynamic data support for a deeper understanding of the mechanical behavior of concrete and promoting a higher level of research and innovation in building materials.