
Under the background of carbon neutrality, the efficient preparation of clean energy such as hydrogen energy has become a research hotspot. The generation, growth and collapse mechanisms of bubbles in electrocatalytic gas production reactions of different materials are different. Traditional observation instruments are limited by time resolution and it is difficult to capture transient details.
Recently, China Science Vision, in conjunction with a new energy laboratory, used high-speed camera technology to track various types of catalytic materials, providing strong support for improving electrocatalytic efficiency and promoting the development of new energy materials.
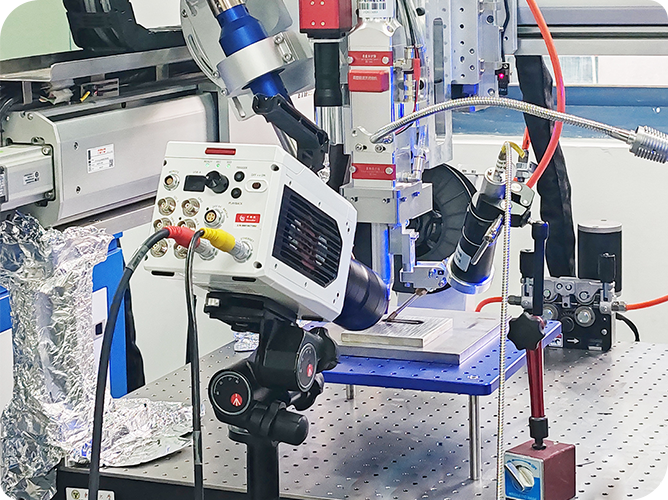
The core observation equipment uses Revealer brand M series small-size, large-memory high-speed camera, which has a high-speed image acquisition capability of 3000fps at 1080P high-definition resolution, and is equipped with an 18x magnification microscope lens, which can achieve accurate analysis of bubble morphology at micron-level spatial resolution.
Other experimental equipment consists of an electrochemical workstation, a three-electrode reaction cell, a six-axis fine-tuning displacement platform, and square glassware.
Step 1: Experimental preparation: Select three electrode materials, platinum, MoS2, and carbon-based composite, and prepare them into long strip-shaped thin sheets. At the same time, prepare H₂SO₄ electrolytes of different concentrations. Place the electrode materials and electrolytes in the reaction pool respectively and connect them to the electrochemical workstation.
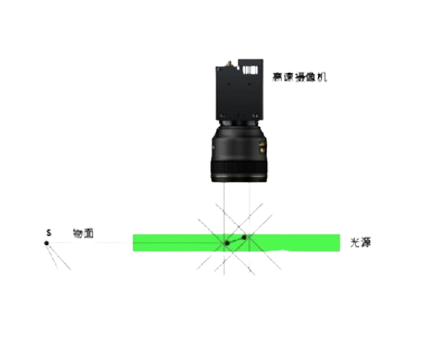
Step 2: Build a high-speed camera: Use backlight illumination, and set up the Thousand Eye Wolf Revealer high-speed camera in front of the glassware, with a magnifying lens, and fine-tune the displacement platform to accurately focus on the 2.5mm×2.5mm observed small field of view.
Step 3: Electrocatalytic reaction: Apply a specific potential to the electrode material through the electrochemical workstation to start the electrocatalytic reaction.
Step 4: High-speed video: Turn on the high-speed camera, match the appropriate frame rate according to the bubble generation rate, and record the dynamic sequence images of bubbles from generation to collapse on the catalytic material.
Step 5: Data processing: Import the captured sequence images into professional image analysis software to quantify the parameters such as bubble size, shape, growth rate and collapse mode. By comparing the bubble dynamic behaviors of the three materials under the same working conditions, their electrocatalytic efficiency is evaluated.
By analyzing the sequence image data captured by the Thousand Eye Wolf Revealer high-speed camera, the dynamic behaviors of bubble generation, growth, and collapse in the electrocatalytic reaction of different materials show differences.
1. Bubble generation stage: On the surface of carbon-based composite materials, the nucleation sites of bubbles are evenly distributed and the nucleation speed is fast, indicating that the carbon-based composite materials have good catalytic activity and bubble generation ability.
2. Bubble growth stage: For carbon-based composite materials, bubbles present regular spherical and ellipsoidal shapes during the growth process, and the growth rate is fast and stable, which is conducive to the rapid escape of bubbles and the continuous reaction.
3. Bubble collapse stage: After the bubbles on the surface of carbon-based materials reach a certain size, they can quickly detach from the electrode surface to form a complete collapse process, while some bubbles on the surface of platinum materials will remain on the electrode surface, hindering the subsequent bubble generation and escape, and affecting the catalytic efficiency.
As a "space-time microscope" in the field of electrocatalytic bubble research, the visualization observation experiment based on high-speed cameras can help researchers gain insight into the transient details of electrocatalytic bubbles with a time accuracy of 0.1μs and a spatial resolution of 5μm, help establish a correlation model between bubble dynamics and current density, and provide a theoretical basis for online monitoring of preparation engineering in the field of new energy.