
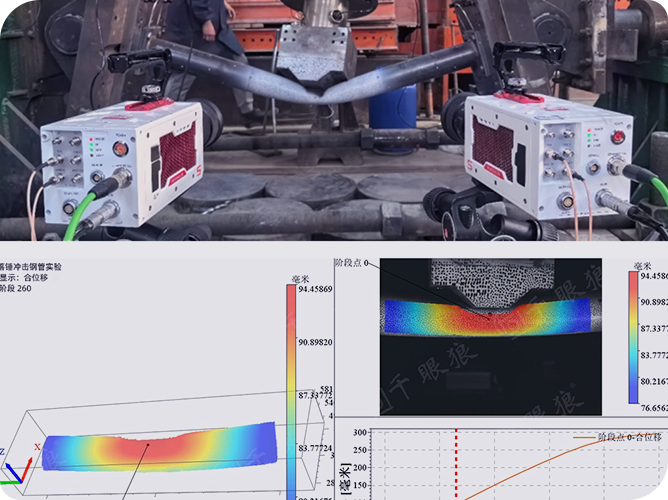

Hey there! If you’ve ever marveled at a slow-motion video of a water droplet splashing or a racecar tire spinning, you’ve seen the magic of a high-speed camera. These incredible devices capture moments too fast for the human eye, turning fleeting seconds into detailed, frame-by-frame stories. Whether you’re a filmmaker, a scientist, or an engineer, understanding high-speed cameras can unlock a world of possibilities. In this guide, we’ll break down what makes these cameras tick, where they’re used, how much they cost, and how to pick the right one for your needs.
For quality control engineers and production managers, high-speed cameras for manufacturing provide critical insights into fast-moving processes that are invisible to the human eye.
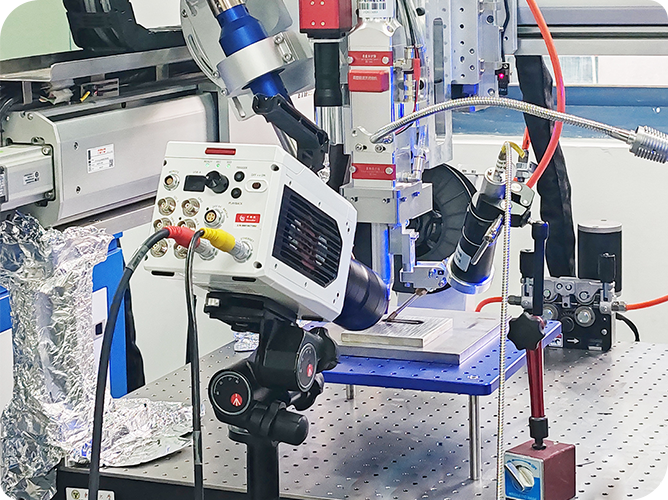
A high-speed camera is a specialized device designed to capture fast-moving events at thousands or even millions of frames per second (fps). Unlike your smartphone’s camera, which typically shoots at 30–60 fps, high-speed cameras can record at 1,000 fps or more, making them perfect for analyzing rapid motion in slow motion. They’re used in industries like automotive, scientific research, and filmmaking to freeze moments that happen in the blink of an eye.
Insight: High-speed cameras are defined by their ability to capture over 100 fps, with professional models often exceeding 10,000 fps for ultra-detailed slow-motion playback.
High-speed cameras rely on advanced sensors, like CMOS or global shutter cameras, to capture images at rapid intervals. The shutter speed—how quickly the camera opens and closes to capture light—is critical. A fast shutter speed (e.g., 1/10,000th of a second) prevents motion blur, while high frame rates ensure every moment is recorded. These cameras often use high-speed CMOS sensors for better light sensitivity and resolution, sometimes up to 8,21 megapixels or more.
Here’s a quick breakdown of key components:
Component | Role | Example Specs |
Sensor | Captures light to create images | CMOS, 5120×4096 resolution |
Shutter | Controls light exposure | Global shutter, 1/100,000s |
Memory | Stores high volumes of data | 320 GB internal memory |
Processor | Handles fast data transfer | 40Gbps fiber interface |
Insight: Global shutter cameras are preferred for high-speed applications because they capture the entire frame at once, avoiding distortion seen in rolling shutter cameras.
High-speed cameras shine in scenarios where precision matters. Here are some top use cases:
· Aerospace: Launch Vehicle Testing and Monitoring, Aerodynamic Testing in Wind Tunnels, In-Flight Component Inspection, Flight Control System Testing, Spacecraft Re-entry Analysis
· Biomedical: Studying Insect Flight and Animal Movement, Analyzing Human Biological Processes, In-Vitro Cell and Tissue Research, Medical Device Testing and Surgical Simulation, Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation
· 3C Electronics/Semiconductors: Semiconductor Chip Manufacturing Process Monitoring, Lithium-Battery Production and Safety Testing, Drop test
· Automotive Crash Testing: Capture airbag deployment or crash dynamics at thousands of fps to improve vehicle safety.
· Scientific Research: Physics Research, ballistics, Fluid mechanics, mechanics of materials, Combustion, energy and power engineering
· Sports Analysis: Analyze an athlete’s golf swing or sprint mechanics in slow motion.
· Manufacturing: Detect defects on high-speed production lines, like in food packaging or electronics.
· Filmmaking: Create stunning slow-motion shots for movies or commercials, like exploding fruit or splashing liquids.
Insight: The automotive industry dominates high-speed camera use due to rigorous safety testing requirements, with over 33% market share in North America alone.
There’s often confusion between high-speed cameras and traffic speed cameras (like those used to catch speeders). Let’s clear it up:
· High-Speed Cameras: Professional tools for slow-motion analysis, used in labs, studios, or testing facilities. They’re not for traffic enforcement.
· Traffic Speed Cameras: Automated devices that monitor vehicle speeds on roads, often using radar or laser technology. In the US, their legality varies by state—California allows them in some areas, but regulations are strict.
If you’re wondering, “Are speed cameras illegal in CA or the US?” the answer depends on local laws. Most states permit them, but usage is restricted to specific zones like school areas. As for “How fast can you go through a 70 mph speed camera?” it depends on the camera’s trigger threshold, typically set 5–10 mph above the limit.
Insight: Misunderstanding high-speed cameras as traffic enforcement tools highlights the need for clear educational content to guide users to the right technology.
High-speed camera costs vary widely, from $1,000 for entry-level models to over $100,000 for professional-grade systems. Understanding the price of high speed camera is crucial for budgeting. Here’s what drives the price:
Factor | Impact on Cost | Example |
Frame Rate | Higher fps (e.g., 100,000+) increases cost | $50,000+ for 100,000 fps models |
Resolution | 2–5 MP cameras are pricier than 0–2 MP cameras | $10,000–$30,000 for 4 MP |
Sensor Type | CMOS or global shutter costs more | $5,000–$20,000 extra |
Memory/Storage | Larger internal memory raises the price | $2,000–$10,000 for 10GB+ |
For example, a high-speed video camera for filmmaking might cost $5,000–$15,000, while a high-speed industrial camera for manufacturing could hit $50,000. Renting is a budget-friendly option, with daily rates starting at $100–$500.
Insight: Advancements in sensor technology are making high-speed cameras more affordable, with the market size projected to reach $2.19 billion by 2034.
Here’s a quick comparison of some top high-speed camera models available through revealerhighspeed.com:
Model | Frame Rate (fps) | Resolution | Key Feature | Approx. Price |
Phantom T2410 | 24270 fps @ 1280×800 | 1280x800 | 84.3% QE,BSI CMOS,256GB | $150,000+ |
Photron Nova S20 | 18750fps @1024×1024 | 1024×1024 | 83%QE, 128GB | $100,000+ |
Revealer NEO 25 | 25,000 @1280×1024 | 1280×1024 | 85% QE,BSI CMOS,320GB | $100,000+ |
Insight: Entry-level models like the Chronos 2.1-HD offer high performance at a lower cost, making high-speed imaging accessible to smaller businesses and hobbyists.
What is considered a high-speed camera?
A camera that captures over 100 fps, with professional models often exceeding 1,000 fps for slow-motion analysis.
What’s the difference between a high-speed camera and a high-speed movie camera?
A high-speed movie camera is a subset of high-speed cameras optimized for cinematic quality, often with higher resolution and color accuracy for filmmaking.
How fast can a high-speed camera record?
Anywhere from 100 fps to over 2 million fps, depending on the model. For example, the i-Speed 7 Series can hit 2.45 million fps.
Are high-speed cameras used in manufacturing?
Yes, high-speed cameras for manufacturing help detect defects in fast-moving production lines, like in food or electronics.
What’s the price of a high fps video camera?
Entry-level models start at $1,000, while professional high-speed digital cameras can cost $50,000 or more.
Are high-speed infrared cameras different?
High-speed infrared cameras capture thermal images at high frame rates, which is ideal for heat pattern analysis in industrial or research settings.
Can high-speed cameras be integrated with existing production lines?
Yes, absolutely. Modern digital high-speed video camera systems are designed for industrial integration. They typically offer standard communication protocols (like GigE Vision, Camera Link, or 10GigE), trigger inputs for synchronized capture with machine cycles, and software development kits (SDKs) for custom automation. They can be mounted on robotic arms, enclosed in protective housings for harsh environments, and connected directly to your factory network or PLC system for real-time or batch analysis of production data.
What's the ROI on high-speed cameras for manufacturing?
The Return on Investment (ROI) for high-speed cameras in manufacturing is typically compelling and can be realized in 6 to 18 months. Tangible benefits include a significant reduction in scrap and rework costs by catching defects early, minimizing production downtime through faster root-cause analysis of machine failures, and improving overall product quality and consistency. Intangible benefits include enhanced process understanding, better design validation, and valuable data for training and continuous improvement initiatives.
Wikipedia. (2025). High-speed photography.
Wikipedia. (2025). High-speed camera.
Grand View Research. (2024). High-speed camera market size, share & trends analysis report.
Mordor Intelligence. (2025). High-speed camera market - size, share & industry analysis.
Gminsights. (2024). High-speed camera market size & share, industry forecasts 2032.
Fastec Imaging. (2018). High-speed cameras for manufacturing.
Vision Research. (2024). Phantom high-speed cameras.
MarketsandMarkets. (2020). High-speed camera market.
Wikipedia. (2025). SPECS (speed camera).
Wikipedia. (2025). Vision Research (company).






