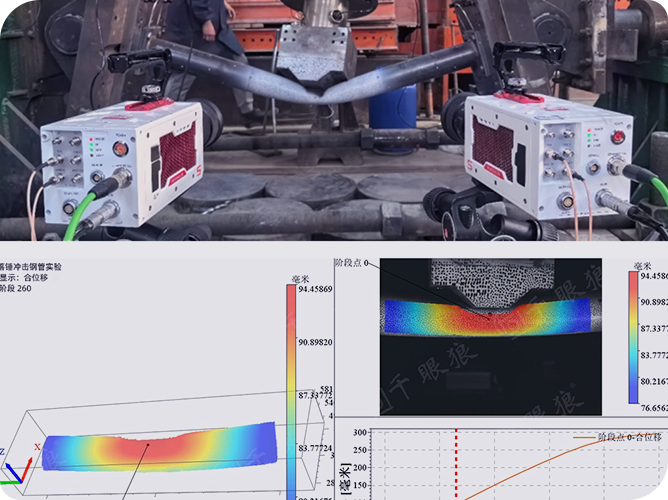

1. Research Background
In the frontier areas of biological and medical research, real-time observation of dynamic processes such as intracellular transport, extracellular matrix reconstruction, and organelles is the key to understanding the mechanisms of life activities, and places stringent requirements on the sensitivity, speed, phototoxicity, and other indicators of the imaging system. Traditional wide-field microscopes are limited by the camera's readout noise and dynamic range, and are unable to capture weak signals of high-speed cell movement under high-power microscopes.
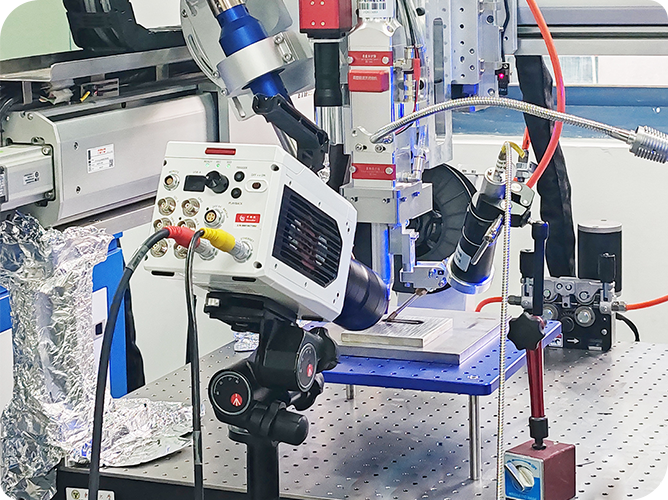
Recently, Revealer technical engineers carried out biological fluorescence imaging tests on the spinning disk confocal microscope system independently developed and built by Yanke Instruments with the Gloria 4.2 sCMOS high-speed and high-sensitivity scientific camera, and collected some fluorescence imaging data of biological samples.
2. Experimental equipment
1) sCMOS scientific camera: Revealer Gloria 4.2, resolution 2048×2048, quantum efficiency ≥95%, high dynamic range 90 dB, readout noise 1.2 e-, frame rate 135 fps.
2) Spinning disk confocal microscope system: independently developed and built by Yanke Instruments.
3. Experimental conditions
Experiment 1
1) Sample: BPAE cells.
2) Spinning disk confocal microscope working conditions: objective lens 60× , 525 nm light source
3) sCMOS scientific camera working conditions: 2024×2024, USB 3.1 interface, 16-bit high dynamic mode, exposure time 10 ms, 46 fps shooting.
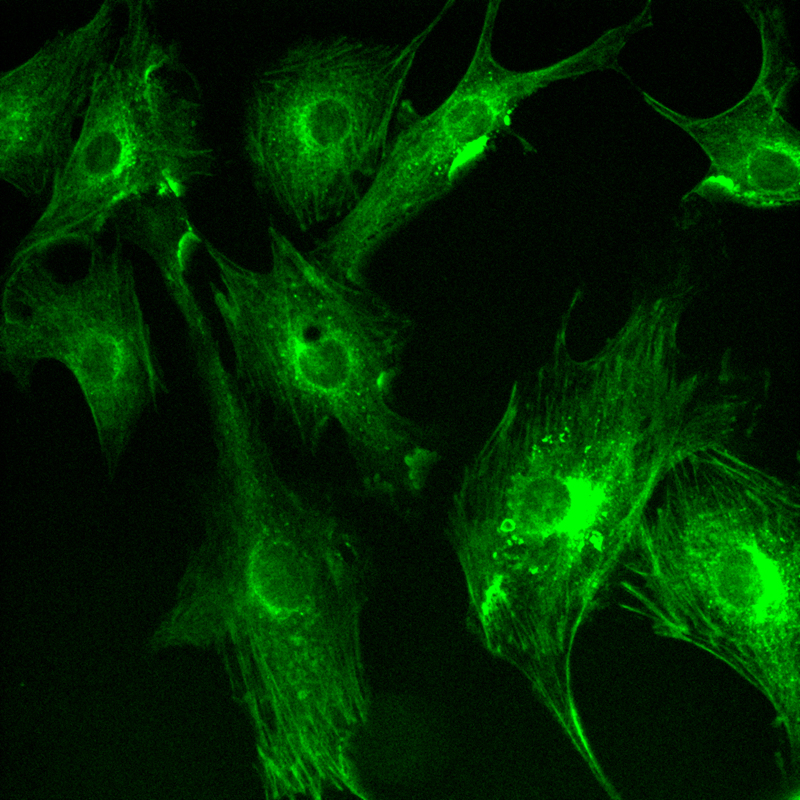
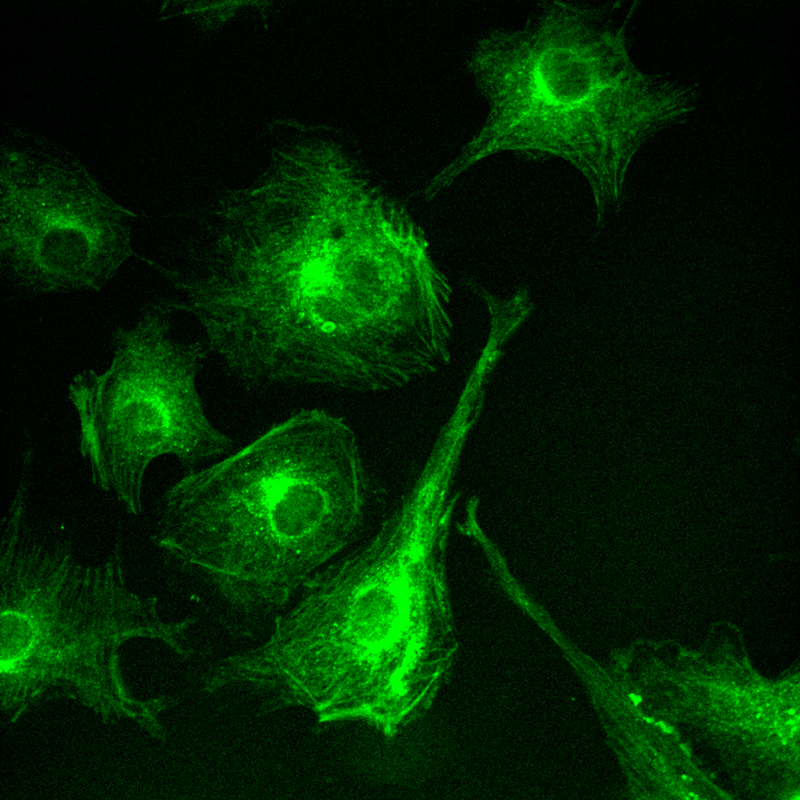
4) Data and results: The experiment clearly demonstrated the interwoven network of microtubules and actin within the cell. Microtubules appeared as long, straight fibrous structures that ran through the entire cell, while actin formed a dense mesh structure at the edge of the cell.
Experiment 2
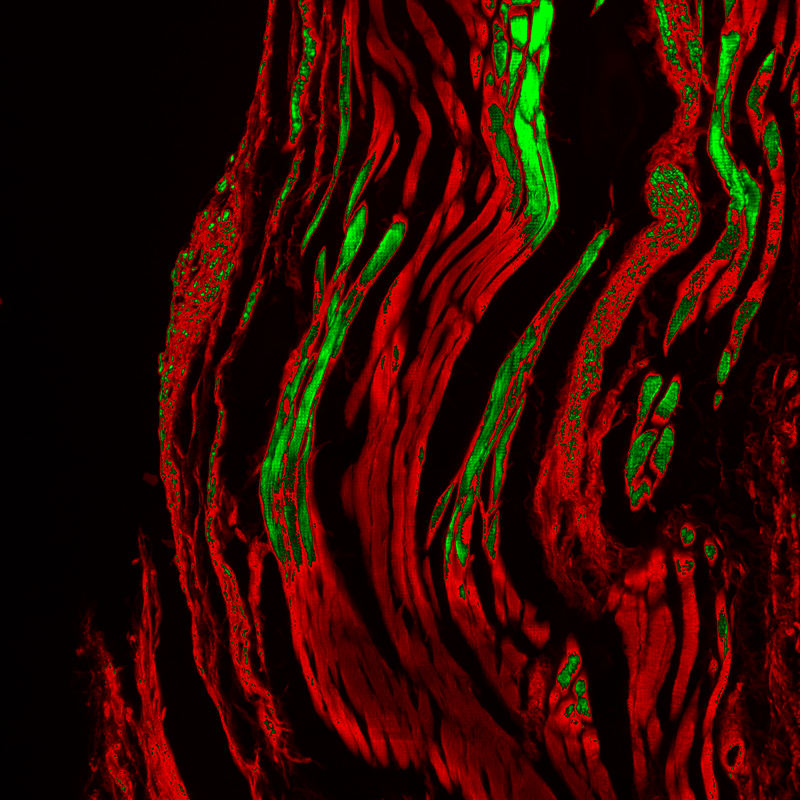
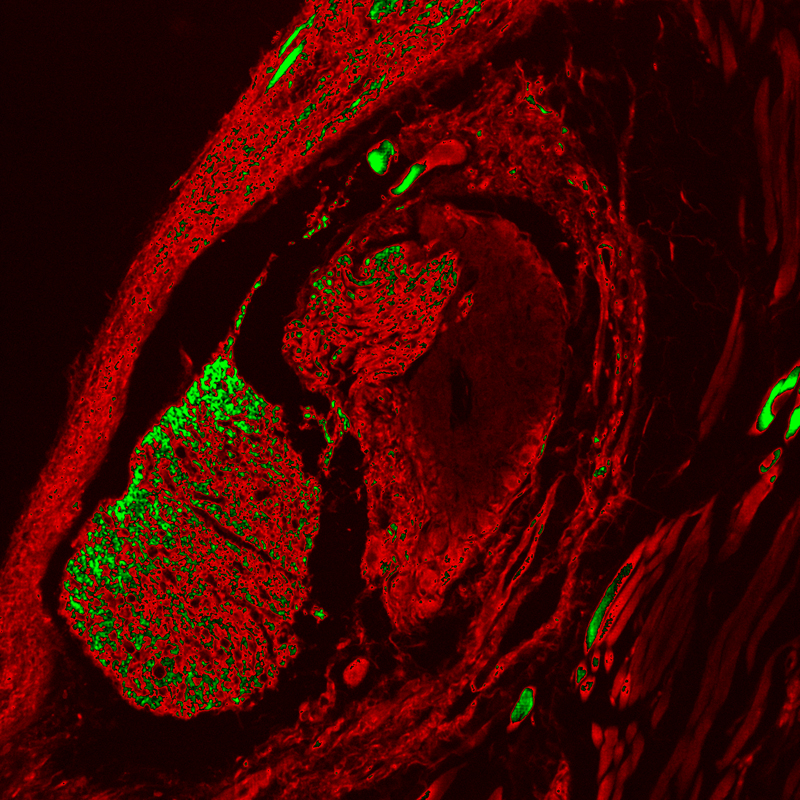
1) Sample: Mouse eye glands.
2) Spinning disk confocal microscope working conditions: objective lens 20x .
3) sCMOS scientific camera working conditions: 2024×2024, USB 3.1 interface, 16-bit high dynamic mode, exposure time 10 ms, 46 fps.
4) Data and Results: The camera successfully captured high signal-to-noise ratio fluorescence images of the ocular gland region, and its signal intensity and spatial distribution characteristics showed significant tissue specificity through ROI analysis.
4. Experimental Conclusions and Prospects
Through fluorescence sampling experiments, the performance of the Revealer sCMOS high-speed and high-sensitivity scientific camera in collecting high-quality fluorescence images in the biomedical field was verified, revealing the technical advantages of the sCMOS scientific camera in high sensitivity, low readout noise, and high-speed acquisition in complex biological scenes with weak signals, sensitivity to phototoxicity, and rapid dynamic changes.
With the continuous breakthroughs in the boundaries of chips and image processing technology, sCMOS high-speed and high-sensitivity scientific cameras will surely provide better quality and clearer low-light imaging solutions for cutting-edge life science research.