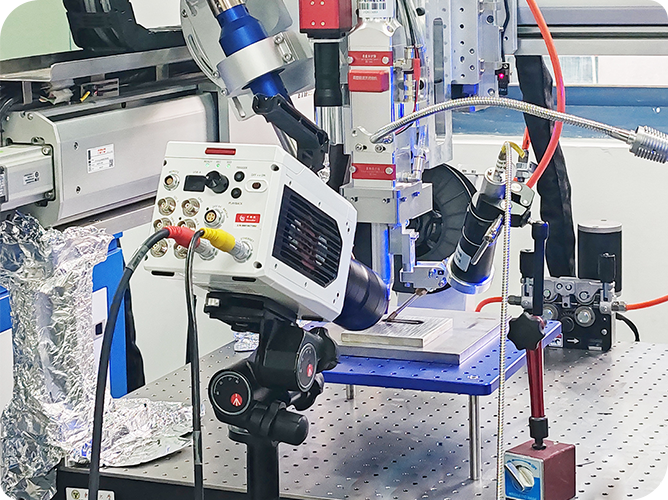
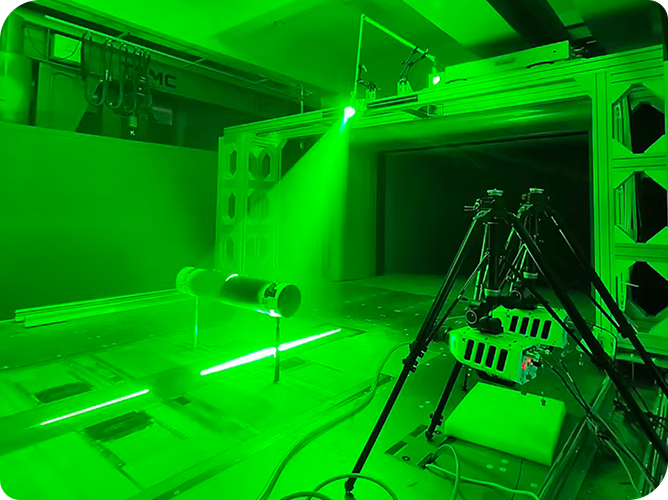
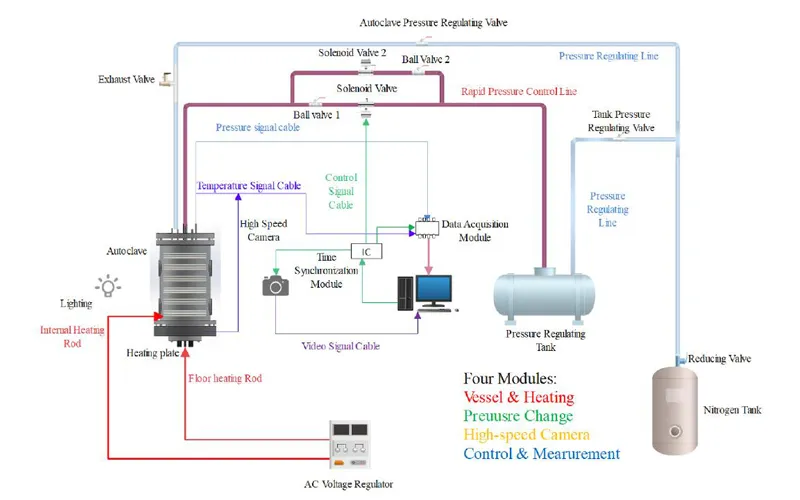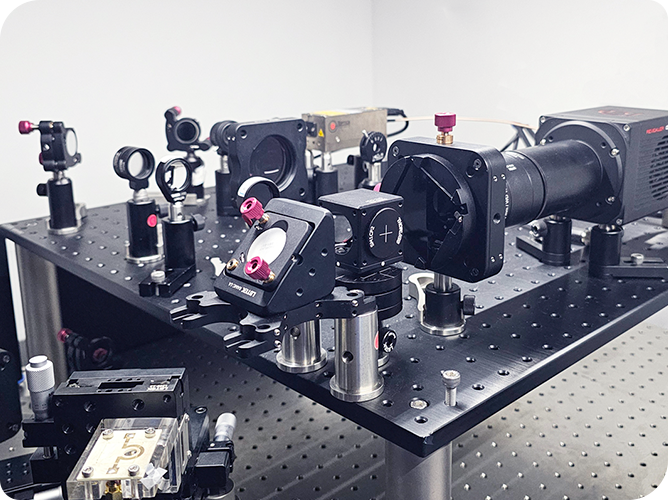

In fluid dynamics experiments, particle image velocimetry (PIV) technology is an important means to study complex flow field structures. The conventional layout of high-speed cameras on the same side will encounter space-constrained scenes such as rotating machinery and compact runners, resulting in limited field of view (Figure 1, left). The R&D engineer of revealer innovatively adopts the high-speed camera opposite side layout scheme (Figure 1 right), and realizes the measurement of the cylindrical circumference flow field through two high-speed cameras from both sides of the water cave, which can effectively avoid the problem of field of view occlusion on the same side layout and improve the data reliability in complex scenarios.

1) Water cave: adjustable flow rate range 0.1~1.0m/s, with 8cm PVC cylindrical model;
2) Revealer PIV particle image velocimetry system: by 2 PIV high-speed cameras, 532nm continuous laser, RFlow4 flow field measurement software.
1) The two PIV high-speed cameras are arranged symmetrically, with an angle of 180° (as shown in Figure 2), the optical axis is perpendicular to the direction of water flow, and the baseline is 50cm away from the center of the cylinder to ensure that the overlapping area of the field of view covers the cylindrical disturbance area.

Figure 2
2) Use a double-layer dot calibration plate to fix it on the displacement platform, put it into the water hole, and perform three-dimensional calibration, and the heat map of the left and right camera's field of view overlap area shows a matching error of < 0.1 pixel.
3) Withdraw the calibration plate, inject tracer particles, turn off the ambient light source, turn on the laser illumination, and align the laser plane with the cylindrical axis.
4) Synchronously trigger two high-speed cameras to collect 500 frames of particle images.
5) The flow field calculation based on the classical PIV-single-channel method, the flow field decomposition analysis based on the Galileo/Reynolds/POD algorithm, and the vortex structure identification analysis based on the Q criterion/λ₂ method were completed using the Revealer flow field measurement software RFlow, so as to verify the effectiveness of the flow field observation method in the opposite layout method.
1) Basic characteristics of flow field:
Hourly average velocity field cloud map, symmetrical Carmen vortex street is formed behind the cylinder, and the velocity in the wake area is reduced.

Figure 3
The pulsating velocity field Reynolds decomposition cloud diagram shows that the high-frequency turbulent kinetic energy is concentrated in the vortex shedding zone.
2) Flow field stability verification
The Galilean decomposition method analyzed that there was no increasing trend in the amplitude of the flow field disturbance velocity (Fig. 4), which confirmed that the flow field was in a stable state and met the basic conditions of analysis.

Figure 4
3) POD modal analysis
The first 3~5 order modes dominate the energy distribution, and the main physical characteristics of the reconstructed flow field have been retained.
The values of the higher-order mode (order 12) are very small, and the cloud graph is basically blue (Fig. 5), indicating that the order 12 and beyond are basically noisy data.
Save the 11th order mode and the amplitude coefficient corresponding to each frame of data, and use the first 3~5 order modes to reconstruct the complete flow field physics characteristics, and then the higher order can bring more flow field details, but at the same time introduce more noise (as shown in Figure 6), specifically using the K order mode, which can be flexibly adjusted according to the experimental goals.

Figure 5

Figure 6
4) Vortex structure recognition
The Q criterion (Fig. 6 left) and λ₂ criterion (Fig. 6 right) were used to calculate the vortex structure, respectively.

Under the Q criterion, the vortex core and the shear layer can be clearly distinguished. The identification of vortex cores and vortex boundaries is the clearest under the λ₂ criterion, but the calculation time is longer.
1) Through precision calibration and synchronous control, the PIV high-speed camera layout on the opposite side can solve the problem of occluding the field of view for shooting on the same side, which has engineering application value in rotating fluid machinery and narrow wind tunnel scenarios.
2) Based on the 2D3C sequence flow field image captured by the opposite layout method, the flow field characteristics are analyzed by using the POD decomposition method of RFlow flow field measurement software, and the core flow structure can be characterized relatively completely and with low noise by using the first 3~5th order intrinsic mode reconstruction.
3) The two criteria for vortex identification can calculate and characterize the process of vortex generation, development, shedding and interaction, the Q criterion can be used as the default method for conventional analysis, and the λ₂ criterion is recommended for refined analysis requirements.