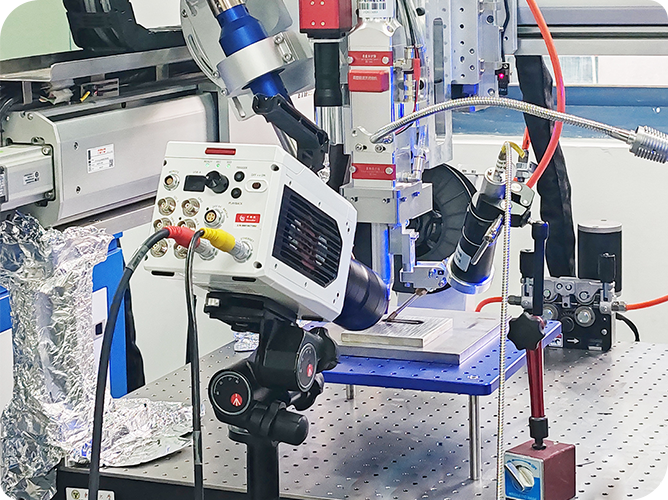
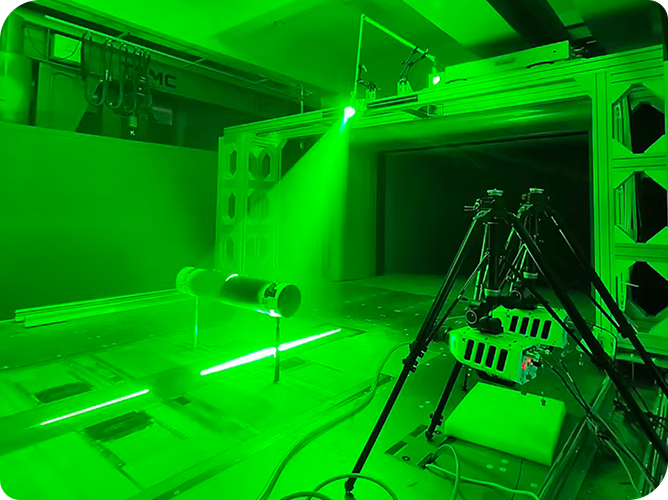
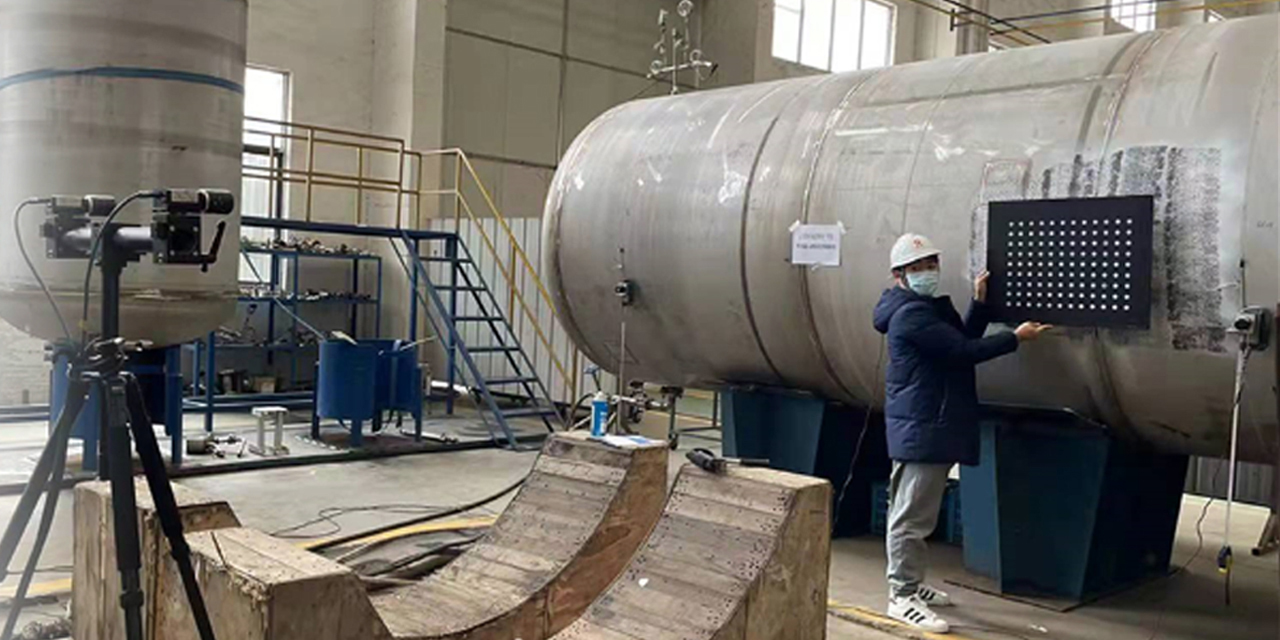
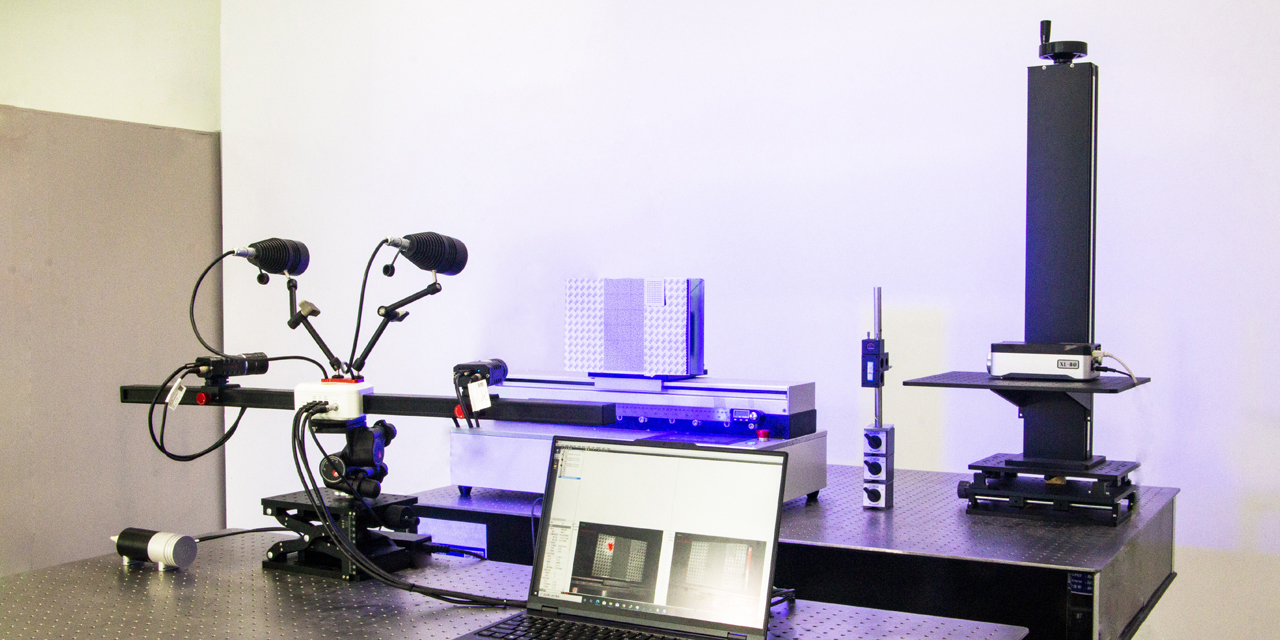
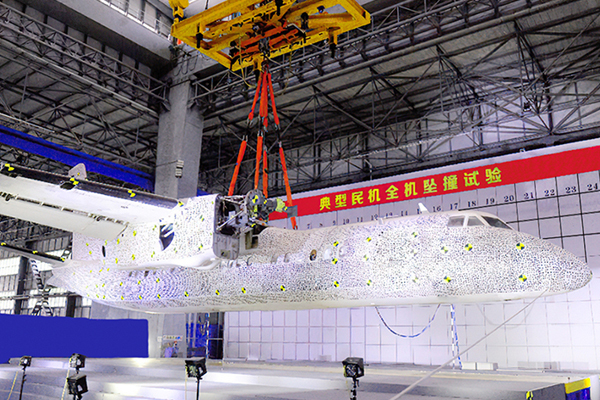
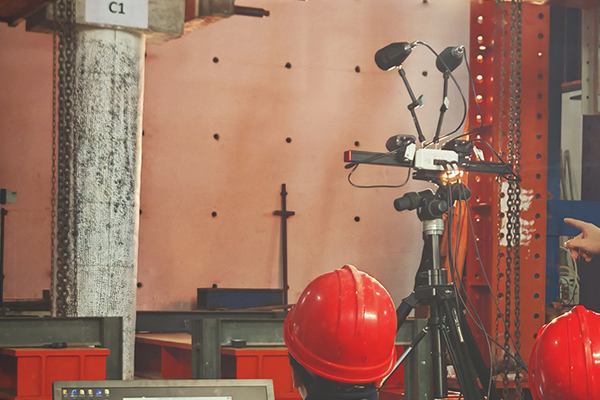
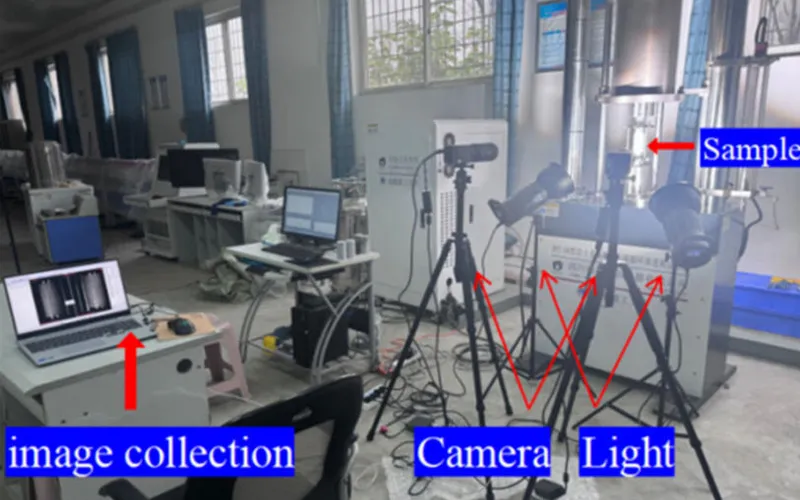
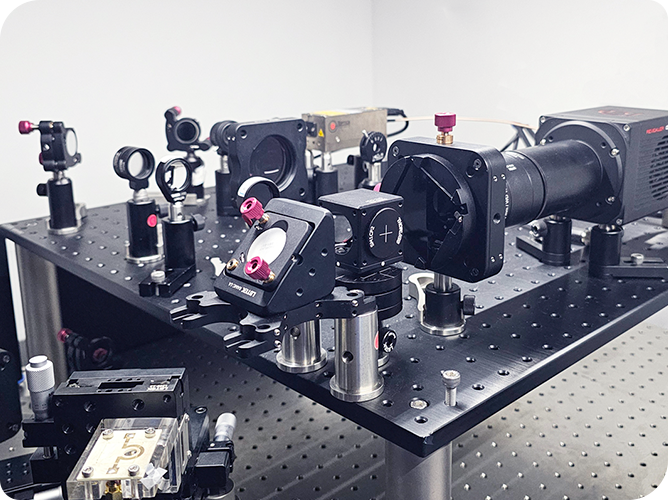
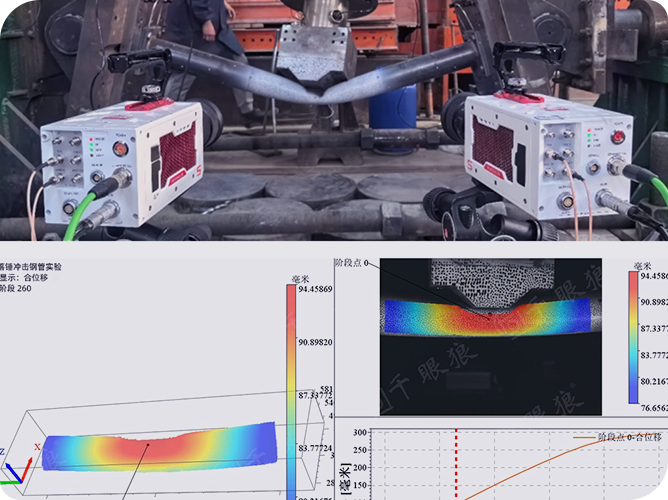
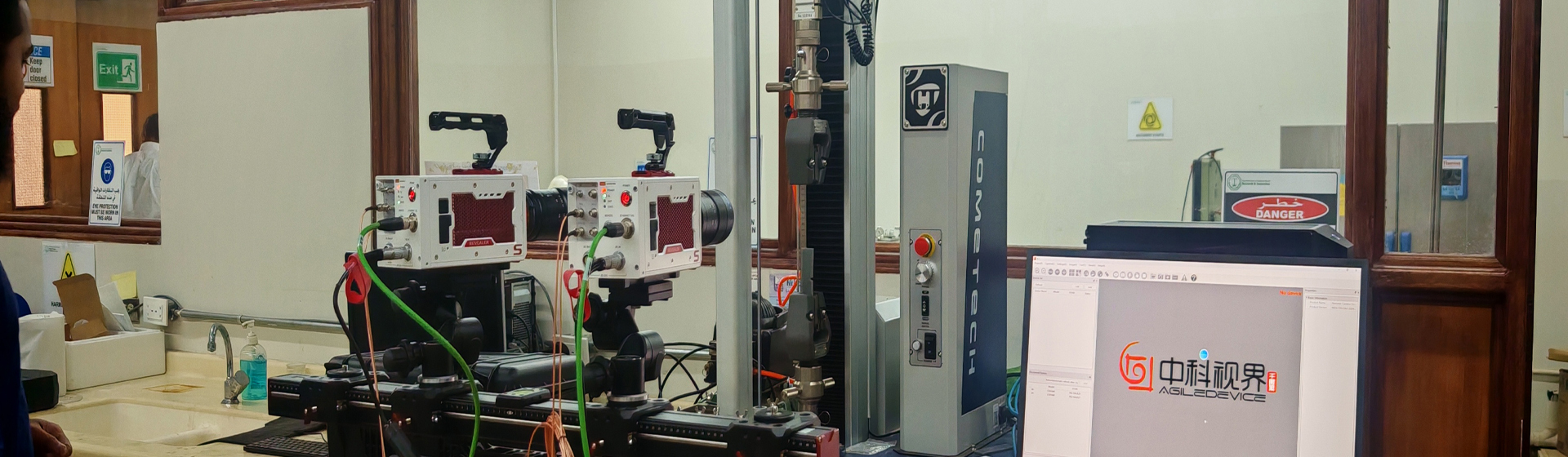
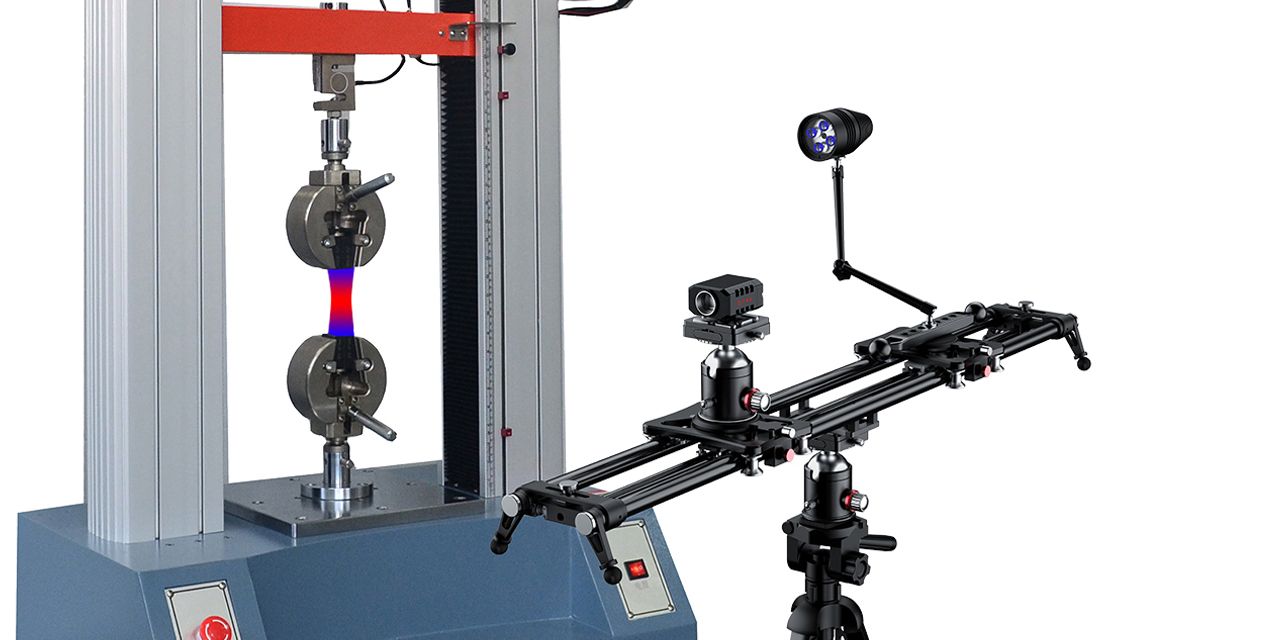
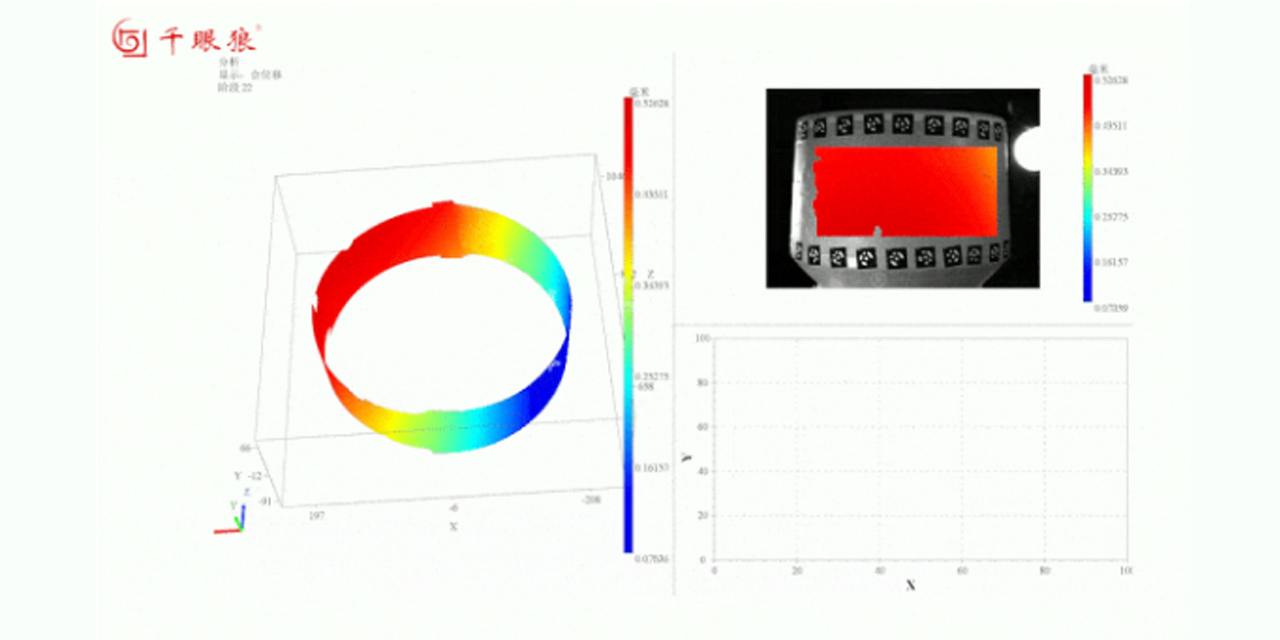
DIC mainly has random errors and systematic errors. Random errors originate from camera noise, while systematic errors come from camera drift, heating, temperature variations, and vibrations. Random errors are quantified through spatial and temporal standard deviations. The spatial standard deviation is calculated by computing the spatial standard deviation of the Quantity of Interest (QOI) for each image, and then averaging the spatial standard deviations of all stationary images in the time domain. The temporal standard deviation is calculated by computing the standard deviation of the QOI for each sub-region in the time domain, and then averaging the temporal standard deviations of all sub-regions within the Region of Interest (ROI).